Puls Cardiac Risk Test
-d4pagm.png)
An Elevated PULS Cardiac Test May Identify:
- Coronary heart disease development
- Presence of unstable/vulnerable arterial plaque
- Increased near-trm risk of a heart attack
Atherosclerotic disease progression is characterized by chronic endothelial damage and an accumulation of fatty plaque within the arterial wall. Unstable plaque can rupture and lead to arterial blockage causing a heart attack. The first steps in prevention are the identification of individuals at near-term risk of a heart attack, and allowing for more aggressive therapy to potentially avoid a future event.
The PULS (Protein Unstable Lesion Signature) Cardiac Test
measures key clinical risk factors including age, sex, diabetic
status, family history of heart attack, and distinct protein
biomarkers. These markers are associated with the biological
pathways underlying cardiac lesion formation, progression and
rupture. This refined methodology of cardiac risk assessment
provides an improved calculation of a patient’s near-term (5 year)
risk for a heart attack.
Clinical Use
The PULS Cardiac Test may be performed on individuals at intermediate risk with one or more risk factors for coronary heart disease.
Clinical Significance
- Cardiovascular risk prediction models such as the
Framingham Risk Score calculate risk of a cardiovascular
event within the next 10 years. When used, these calculations
rely heavily on established clinical risk factors1 which may not
fully estimate the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the
general population.2,3 - The PULS Cardiac Test measures clinically significant
proteins in the blood associated with active unstable lesion
formation and when combined with established clinical risk
factors, predicts whether a cardiac lesion could rupture
within a 5 year period.4
- In the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), the PULS Cardiac Test outperformed a common risk calculator, yielding a net reclassification index of 42.7% in individuals defined as intermediate risk by the Framingham Risk Score.4 Reclassification of those initially defined as intermediate risk to high risk may result in more appropriate therapeutic intervention.
- In a large clinical trial, the PULS Cardiac Test identified 61% of
patients who went on to have a cardiac event who otherwise
would have been missed using established risk factors alone.5
Testing Frequency
The frequency of ordering The PULS Test is determined by an
individual’s medical history, but may be monitored more frequently
in those at moderate to high risk for cardiovascular disease.
Sample Type
The PULS Cardiac Test should be performed on a serum and EDTA whole blood sample. Patients do not need to fast for the test.
Biomarkers:
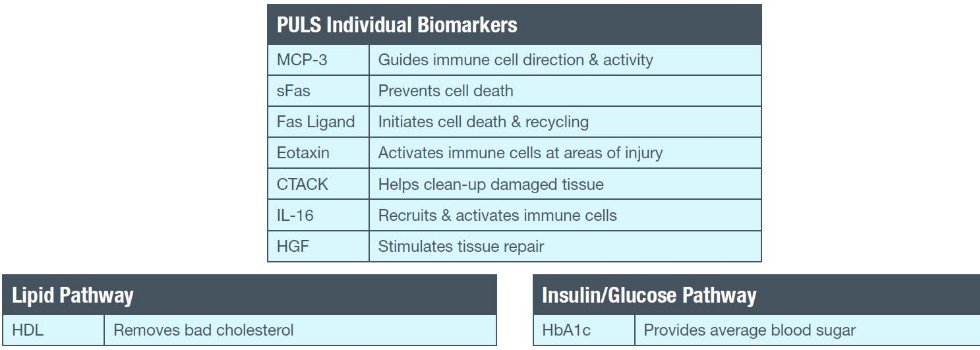
-lxthod.png)
-ombwkc.png)
-le2flw.png)
If you have any further questions about the PULS Cardiac Test, please email our technical support team:
References
1. Wilson PW et al. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation. 1998; 97: 1837-1847.
2. Greenland P et al. Major risk factors as antecedents of fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease events. JAMA. 2003; 290: 891-897.
3. Khot UN et al. Prevalence of conventional risk factors in patients with coronary heart disease. JAMA. 2003; 290: 898-904.
4. Cross DS et al. Coronary risk assessment among intermediate risk patients using a clinical and biomarker based algorithm developed and validated in two population cohorts. Curr Med Res
Opin. 2012; 28: 1819-1830.
5. Simonini A and Harrington DS. Early detection of unstable cardiac lesions in asymptomatic individuals at risk of acute coronary syndrome. Cardiology. 2015; 131: 148.
-rhmih2.png)
Also available from Cleveland Heart Lab:
Advanced Blood Chemistry




